There’s a difference between heart attack vs. sudden cardiac arrest, but it’s not always clear which is which. Despite their similarities and distinctions, both require immediate treatment and care. Whether you work in the healthcare field or not, it’s good to know how to recognize cardiac arrest and a heart attack and what you can do to increase the afflicted person’s likelihood of survival. Read on for the basics of identifying and reacting to both.
How Do Heart Attacks Happen?
A heart attack is also known by its more technical term of myocardial infarction. Heart attacks are brought about when an individual’s artery or arteries become blocked with what is known as plaque. Plaque is created by an overabundance of cholesterol from fatty foods such as dairy and meat products. The cholesterol enters the bloodstream and begins to collect in the arteries. White blood cells attack the cholesterol, but this builds up greater inflammation and fat. Eventually, the artery becomes capped, or the plaque breaks and forms a clot. The artery is unable to deliver oxygen to the heart, causing part of the heart muscle to die. In time, this can cause a heart attack.
What Does a Heart Attack Look Like?
Continuing our assessment of the difference between heart attack vs. sudden cardiac arrest, the symptoms are varied. Men tend to exhibit shortness of breath, a squeezing sensation in the chest, sweating, and pain in the neck, shoulders, arm, and jaw. Women, however, can feel dizzy, nauseated, weak, and have pain between their shoulder blades. In any event, if the patient is rushed to the hospital within 90 minutes, they have a particularly good chance of survival. Heart attack victims tend to remain conscious and should not be given CPR or have an AED applied to their chest. Speedy care is the best medicine.
What Is Sudden Cardiac Arrest?
Sudden cardiac arrest is more abrupt than a heart attack because the heart immediately stops beating, causing the person to become unconscious and stop breathing. During cardiac arrest, no blood is sent to the brain and other vital organs, leading to brain damage and, shortly, death. Survivors report symptoms such as shortness of breath, seizures, nausea, and chest pains, but they may collapse before describing these sensations.
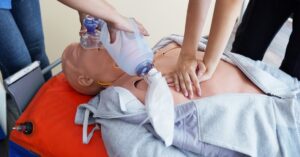
What To Do for Cardiac Arrest
Hopefully, you’ll have attended AHA CPR and AED classes explaining the proper application of CPR and AED usage. Deliver CPR to the person to ensure blood keeps flowing in the body, bringing whatever oxygen is left to their organs. In between this, an AED can check their heart rhythm and determine whether and when to deliver a shock to restore its usual healthy rhythm. In this case, milliseconds count. Swift action can increase the patient’s chances of survival.