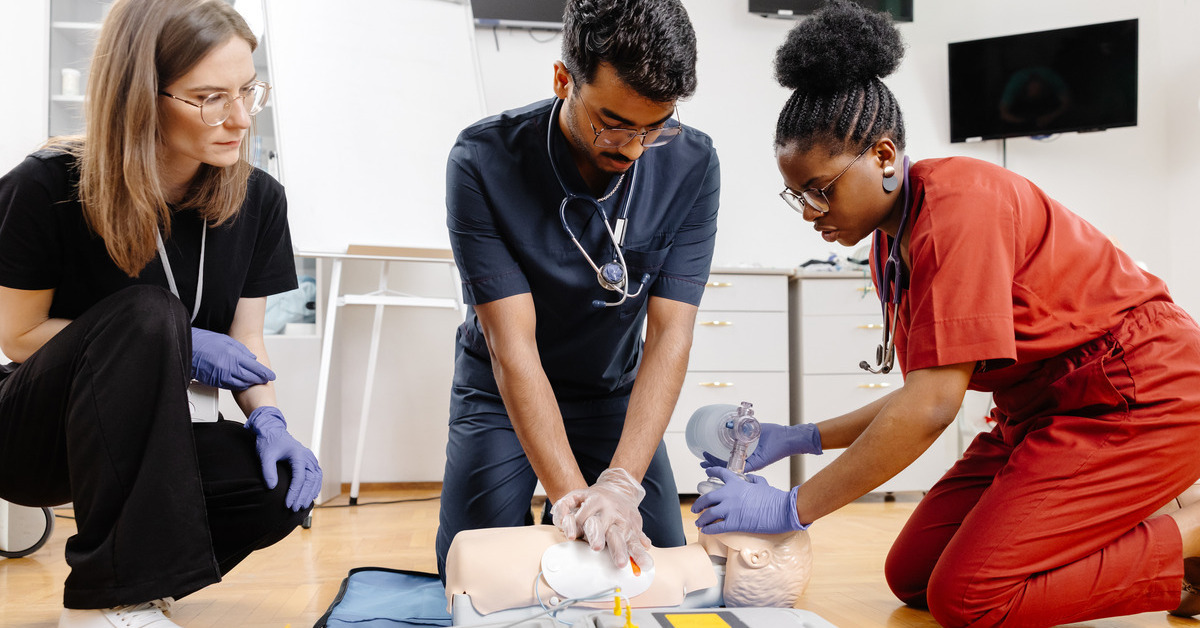
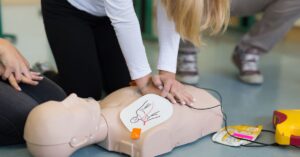
Cultural diversity enriches communities, but it also poses challenges in diverse fields, including CPR training. Ensuring effective rescue training across various cultural backgrounds is key for widespread preparedness during emergencies. Explore how healthcare professionals and trainers can begin addressing cultural barriers in CPR training to establish a more inclusive learning environment.
Understanding Cultural Barriers in CPR Training
Cultural differences can significantly impact CPR training outcomes. Here are some common challenges:
- Language barriers: Non-native English speakers may struggle to understand instructions or technical terms, leading to misunderstandings during training.
- Cultural taboos: Practices such as touching the chest area or engaging in mouth-to-mouth resuscitation may be inappropriate in certain cultures.
- Diverse learning styles: Different cultural backgrounds may influence how individuals learn best, whether through visual aids, hands-on practice, or verbal instruction.
- Preconceived notions about authority: Some individuals may hesitate to challenge instructors or ask questions, fearing they will appear disrespectful.
These barriers can hinder the learning process, reducing confidence and ability when it comes to performing life-saving skills under pressure.
How the AHA BLS Course Bridges Cultural Gaps
The American Heart Association Basic Life Support (AHA BLS) course is designed to address these challenges and create an inclusive training experience. Here’s how:
Hands-On Skills Training
The AHA BLS course with skills training goes beyond lectures to include hands-on CPR practice, which accommodates learners who thrive through physical demonstration. This approach helps trainees from diverse cultural backgrounds internalize techniques like chest compressions and ventilation.
Interactive, Flexible Learning Formats
The course includes interactive teaching methods, such as group discussions, role-playing, and videos, which cater to varied cultural learning styles. Trainers are encouraged to create a supportive atmosphere where asking questions and seeking clarification are key to building confidence.
Focus on Clear, Multilingual Communication
AHA materials often provide translations and simplified language, allowing trainers to deliver concepts clearly to non-native speakers. The emphasis on universally understood visuals ensures more inclusive communication.
Encouraging Cultural Sensitivity Among Trainers
Highly trained instructors help break down cultural stigmas by fostering respect and communication throughout the session. They guide students in practicing scenarios within culturally appropriate boundaries while emphasizing the universal value of CPR skills.
Scenario-Based Training
By incorporating realistic case scenarios, the BLS course prepares participants for emergencies with diverse cultural considerations. Trainees better understand how to adapt to someone’s cultural or personal sensitivities during a crisis.
Creating a Path Toward Inclusive Life-Saving Skills
Cultural barriers should never stand in the way of saving lives. Healthcare professionals and CPR trainers play a vital role in guaranteeing everyone—regardless of background—has access to effective training. By addressing cultural barriers in CPR training, trainers can foster inclusion while providing essential skills for trainees to build confidence and cultural sensitivity.
If you’re ready to improve inclusivity in your CPR programs, consider enrolling in or facilitating an AHA BLS course. Build a more prepared and unified community today!