Healthcare professionals understand the importance of staying updated with the latest CPR guidelines. This knowledge saves lives and ensures you can maintain the highest standard of care. We provide a comprehensive guide to the latest updates in CPR guidelines in this post to enhance your understanding of this life-saving technique.
Why Keeping Up With CPR Guidelines Matters
Staying updated on CPR guidelines is a mandatory step toward better compliance, competence, and confidence in providing stellar care for patients. Updated guidelines incorporate the latest scientific research, offering the most effective techniques for reviving someone experiencing cardiac arrest. By keeping up-to-date, you ensure your skills remain sharp and effective.
Critical Updates in Adult CPR
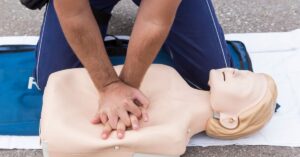
Compression-Only CPR
One of the significant updates is the emphasis on compression-only CPR for adults in out-of-hospital settings. This simplified technique focuses on providing chest compressions at 100–120 compressions per minute. This method is highly effective in the early stages of cardiac arrest.
Optimal Compression Depth and Rate
The recommended compression depth for adults is now between 2 to 2.4 inches. Maintaining this depth ensures adequate blood flow to vital organs and a 100-120 compressions per minute compression rate. This technique maximizes the chances of survival.
Simplified CPR Algorithm
The latest updates have also introduced a streamlined CPR algorithm that focuses on quick cardiac arrest recognition, immediate activation of emergency services, and prompt initiation of chest compressions. Implementing an automated external defibrillator (AED) as soon as possible is also crucial.
Updates in Pediatric CPR
Age-Appropriate Techniques
The latest updates emphasize age-specific techniques for pediatric patients. The recommended compression depth for children and infants is approximately 1.5 inches, and the compression rate remains at 100-120 per minute. These adjustments ensure that CPR is effective, given the physical differences between children and adults.
Continuous Chest Compressions
Continuous chest compressions are the best approach when advanced airway management is not immediately available. This technique involves delivering compressions without the traditional 30:2 compression-to-ventilation ratio, which helps maintain blood flow during resuscitation.
Use of AEDs in Pediatric Cases
AEDs are becoming increasingly user-friendly and many professionals now use them in pediatric cases. These devices can analyze the child’s heart rhythm and deliver a shock tailored to pediatric needs.
The Role of Technology in CPR
Advancements in technology have significantly impacted CPR guidelines. Devices such as AEDs and real-time feedback tools for chest compressions have become standard. These technologies provide immediate feedback, ensuring that professionals deliver compressions effectively and at the correct rate and depth.
Advanced Airway Management
Advanced airway management is a critical skill for most healthcare professionals. The latest guidelines recommend minimizing interruptions in chest compressions when securing an airway. A healthcare professional must perform techniques such as endotracheal intubation quickly and efficiently in some cases to maintain oxygenation and perfusion.
Updates in Senior CPR

Considerations for the Older Adult Population
When performing CPR on older adult patients, several unique factors come into account due to the physiological changes associated with aging. Many seniors have underlying conditions, which could complicate resuscitation efforts. Therefore, approaching CPR with a clear understanding of potential complications, such as osteoporosis, frailty, or the presence of implanted devices is crucial.
Adjusted Compression Techniques
While the general compression depth and rate guidelines remain relevant, healthcare professionals should be particularly cautious when administering chest compressions to elderly patients. A compression depth of approximately two inches is standard, but gauging the individual’s body condition and adjusting your anatomy-specific performance accordingly is vital. Adjusting performance prevents injury while still being effective.
Monitoring for Feedback
Constant monitoring is vital when performing CPR on seniors. Healthcare professionals should examine changes in the patient’s condition and readiness for rescue breaths or other interventions. In addition, you should adapt AED use to suit the older adult’s needs, ensuring that the device provides appropriate care without causing undue stress.
Emphasizing Post-Resuscitation Care
Post-resuscitation care for older adult patients can be complex. Following the initial stabilization through CPR, evaluating and addressing pre-existing conditions that could contribute to the cardiac event is essential. Inspecting includes a comprehensive assessment and collaboration with other healthcare professionals to ensure long-term recovery and heart health.
The Significance of Team Dynamics
CPR is often a team effort. Remaining communicative across the team ensures all team members can coordinate a successful outcome. The latest guidelines emphasize the importance of clear roles and responsibilities, with one person leading the resuscitation efforts to ensure a coordinated approach.
Training and Regular Updates
Regular training and updates are essential for maintaining proficiency in CPR. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends refresher courses every two years. These sessions update healthcare professionals on the latest guidelines and provide hands-on practice to keep skills sharp.
Ethical Considerations in CPR
Ethical considerations are an essential aspect of CPR. Healthcare professionals must know the patient’s wishes, including do-not-resuscitate (DNR) orders. Understanding and respecting these directives is crucial in providing ethically sound care. Here are other ethical decisions to know before attempting CPR.
Patient Autonomy
Respecting a patient’s autonomy involves acknowledging their right to make informed decisions about their care. For instance, it is imperative to follow a patient’s do-not-resuscitate (DNR) order, even if bystanders urge you to try. Not honoring a DNR can lead to legal consequences and distress for the patient’s family and the healthcare team.
Beneficence and Nonmaleficence
Healthcare professionals must always strive to act in the patient’s best interest, balancing beneficence (doing good) with nonmaleficence (not harm). For example, in cases where a patient’s condition is unrecoverable, extensive resuscitation efforts may prolong suffering rather than provide a benefit. In such scenarios, it may be more ethical to prioritize comfort measures over aggressive resuscitation.
Informed Consent
In cases where patients cannot communicate their wishes, such as in emergencies, the standard ethical practice is to act in line with what a reasonable person would choose. However, involving the patient’s family members in the decision-making process and seeking their insight into the patient’s previous wishes and values is crucial.
Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural beliefs significantly influence attitudes toward CPR and end-of-life care. For example, some cultures may prioritize spiritual or familial approaches over clinical interventions. Healthcare providers must be aware of these values and integrate them into their care plans, ensuring you respect the rights and beliefs of patients and their families.
Staying on Top of CPR Guidelines Is As Easy as 123
Incorporating the tips from this guide to the latest updates in CPR guidelines into your practice is about saving a life under updated protocols. By staying informed and continually updating your skills, you contribute to improved patient outcomes. Explore reputable sources and consider ongoing education opportunities for a more detailed guide to the latest updates in CPR guidelines.
Don’t hesitate to explore the most recent CPR guidelines with an online CPR course if you want to deepen your understanding. Sign up for a healthcare provider course online to prepare and continue to make a difference in CPR-related emergencies. CPR123 is here to make CPR certification possible and more accessible to healthcare professionals.